Sulfur: An Essential Element in Industry and Biology
Sulfur (S) is a ubiquitous, multivalent nonmetal element. Under normal conditions, it appears as a tasteless, odorless, yellow crystalline solid. While sulfur is often associated with the foul smell of rotten eggs, that odor actually comes from hydrogen sulfide (H2 S), a sulfur compound, not the elemental sulfur itself.
Sulfur is the fifth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and the tenth by mass on Earth. Its abundance and unique properties make it a critical raw material for countless industries and an essential element for all living organisms.
Biological Significance of Sulfur in the Body
Sulfur plays a fundamental and essential role in human biology, accounting for approximately 0.25% of the human body weight.
Why the Body Needs Sulfur and Its Essential Processes
The body requires sulfur for several vital processes:
-
Protein Structure: Sulfur is a core component of essential amino acids, specifically methionine and cysteine. The sulfur atoms in cysteine form disulfide bonds, which are critical for maintaining the complex 3D shape and stability of many proteins (including keratin and collagen), enzymes, and antibodies.
-
Detoxification: Sulfur is essential for the body’s primary detoxification pathways in the liver, where it helps convert toxins into harmless substances that can be excreted.
-
Antioxidant Defense: Sulfur is a key component of glutathione, one of the body’s most powerful natural antioxidants, which protects cells from oxidative stress and damage.
-
Metabolism: It plays a role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and is necessary for the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) and B vitamins (like thiamine and biotin).
Effect of Sulfur on the Skin
Sulfur is widely used in dermatology for its therapeutic properties:
-
Antiseptic and Keratolytic Action: Sulfur has mild antiseptic and antifungal properties. Its primary effect is keratolytic, meaning it helps to soften and shed the outer layer of the skin. This makes it effective in treating conditions like acne, rosacea, and seborrheic dermatitis.
-
Pore Cleansing: It helps to clear clogged pores and reduce inflammation associated with breakouts.
Potential Side Effects of Sulfur for the Body
While essential, excessive or inappropriate exposure to certain sulfur compounds can have side effects:
-
Topical Use: Dermatological products containing sulfur can cause skin irritation, dryness, redness, or a peeling sensation, especially at high concentrations.
-
Dietary: For healthy individuals, dietary sulfur is generally safe. However, in rare cases, sulfur allergies or high intake of sulfates can cause mild gastrointestinal upset.
-
Inhalation (Hydrogen Sulfide): The most dangerous side effect comes from inhaling highly toxic sulfur compounds like hydrogen sulfide (H2 S), which can cause irritation of the eyes and respiratory system, and, in high concentrations, death.
Main types of sulfur based on physical form:
Sulfur is available in various forms such as granular, lumpy and powdered.
Granular sulfur: Used for the production of sulfuric acid, sulfur fertilizer and sugar bleaching.
Lumpy sulfur: Used for conversion into very fine powders and also in sulfuric acid production plants.
Powdered sulfur: Used mostly in agriculture as a pesticide.
The choice of the type of sulfur depends on its application. For example, granular sulfur is better for soil amendment, while powdered sulfur is suitable for spraying.
Key Industrial Uses
-
Sulfuric Acid Production: The single largest application of sulfur globally (about 85-90%) is in the production of sulfuric acid (H2 SO4). This essential chemical is used in manufacturing phosphate fertilizers, petroleum refining, metal processing, and production of chemicals like dyes and detergents.
-
Agriculture: Sulfur is the fourth most important nutrient for plants. It is used as a fertilizer (in the form of Granulated sulfur or sulfur-bentonite mixtures) to amend alkaline and saline soils, improve water penetration, and help plants better utilize nitrogen. Powder sulfur is also used as a natural fungicide and pesticide. Sulfur purity is confirmed by Sulfur analysis.
-
Refining and Petrochemicals: Sulfur is a major byproduct of refining crude oil and natural gas (often referred to as Petroleum products sulfur). This petrochemical sulfur has a very high purity (around 99.5%) and is preferred in most industrial applications. The refining process separates sulfur from fuels like Gasoline and kerosene.
-
Other Applications:
-
Rubber Industry: Sulfur is crucial for the vulcanization of rubber, giving it strength and elasticity.
-
Chemicals: Used in manufacturing gunpowder, matches, dyes, and synthetic fibers.
-
Oils: Sulfur content is important in the quality and application of Base oil.
-
Conclusion
Sulfur, whether in the form of Clumped sulfur, high-purity petrochemical Granulated sulfur, or fine Powder sulfur, is indisputably one of the world’s most vital elements. From enabling life’s fundamental biological processes to forming the backbone of global industries like refining and agriculture, its importance is immense. The high-purity sulfur derived from Petroleum products is key to manufacturing essential compounds and clean fuels like diesel.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sulfur used for?
Sulfur has a wide range of applications. Its primary use is in the production of sulfuric acid, a vital substance in chemical manufacturing, fertilizer production, and metal processing. It is also used in agriculture as a fertilizer and pesticide, in the rubber industry for vulcanization, and in the production of matches, explosives, and some skin medications.
Is sulfur toxic to humans?
Elemental sulfur has low toxicity. Skin contact or inhalation of small amounts generally does not pose a serious risk. However, inhaling large amounts of sulfur dust can cause respiratory irritation. Some sulfur compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide, are highly toxic.
What does sulfur do to your body?
Sulfur is an essential element for the human body. It is a key component of two important amino acids (methionine and cysteine), which are crucial for protein synthesis. Sulfur also plays a vital role in metabolic processes, skin, hair, and nail health, and the function of enzymes and vitamins.
Where is sulfur found?
Sulfur is found naturally in mines, particularly in volcanic regions, as well as in sulfide and sulfate minerals. However, most of the sulfur used today is obtained as a byproduct of petroleum and natural gas refining.
What does sulfur do to skin?
Sulfur has antibacterial and antifungal properties. For this reason, it has been used in the past and is still found in some skincare products to treat conditions like acne, psoriasis, and scabies. Sulfur helps to reduce oiliness on the skin and fights bacteria that cause breakouts.
Is sulfur in eggs?
Yes, eggs are a rich source of sulfur compounds. Sulfur is found in the amino acids within both the egg white and the yolk. The characteristic smell that can be noticed when cooking eggs is due to these sulfur compounds.
What does sulfur smell like?
Pure sulfur is odorless. The smell often associated with sulfur (like rotten eggs) is actually from hydrogen sulfide gas (H2S), a sulfur compound.
What does sulfur keep away?
The smell of sulfur is unpleasant to some animals and insects, particularly snakes and lizards. It is sometimes used as a repellent to keep these animals away from specific areas.
Is sulfur bad for your hair?
No, sulfur is essential for healthy hair. It is a key component of the protein keratin, which is the main building block of hair. A deficiency can lead to weak and brittle hair. However, excessive use of sulfur-based hair products can cause scalp dryness in some individuals.
Is coffee high in sulfur?
Yes, coffee contains sulfur compounds. These compounds contribute to the complex aroma and flavor of coffee. The amount of sulfur varies depending on the bean type and roasting process.
What does sulfur do to your brain?
Sulfur is vital for brain function. It is involved in the synthesis of certain neurotransmitters and in the brain’s detoxification processes. Sulfur helps the body produce glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that protects brain cells from damage.
Can I take sulfur every day?
Taking sulfur supplements is not recommended without consulting a doctor. Sulfur is naturally obtained through a balanced diet (including foods like garlic, onions, eggs, meat, and cabbage). Excessive intake of supplements can lead to digestive issues.












The article mentioned that there are different types of sulfur, and some aren’t suitable for agriculture. How can I ensure that the sulfur I’m buying for my farm or plants is of high quality and safe for the soil and crops? What characteristics should I look out for?
That’s a very important and practical question, as choosing the right sulfur for agriculture directly impacts your soil and crop health. Based on the article, to ensure the sulfur you’re getting is high-quality and suitable for agricultural use, you should pay attention to the following points:
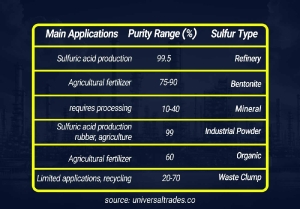
Sulfur Source: The article states that Petrochemical Sulfur, derived from natural gas and oil processing, is the best option for agriculture due to its very high purity (around 99.5%) and lack of harmful contaminants. In contrast, Mineral Sulfur has lower purity (10-40%) and might contain toxic elements like aluminum, making it unsuitable for agriculture unless properly processed. So, look for sulfur that is specified as petrochemical in origin.
Purity Level: Agricultural sulfur, especially Bentonite Sulfur (as mentioned in the article), is typically available with 75% or 90% sulfur content. These high purity percentages indicate better quality and effectiveness. Industrial powdered sulfur with around 99% purity is also suitable for agricultural use.
Physical Form and Formulation: Granular Sulfur is better for soil amendment and nutrient supply as it releases slowly into the soil. Powdered Sulfur is mostly used as a pesticide and needs to be very pure. Bentonite sulfur, due to its bentonite content, helps with water absorption and better dispersion in the soil, increasing nutrient availability for plants.
In the section on sulfuric acid production, you mentioned that this acid is one of the most important chemicals in various industries, with about 85-90% of global sulfur production being used for this purpose. Given the high importance of sulfuric acid in diverse industries (such as fertilizer production, metal processing, and oil refining), could you briefly explain why this substance is so widely used and vital? What unique properties does it possess that have earned it the title “King of Chemicals”?
You’re most welcome; I’m glad the article provided you with useful information. Yes, sulfuric acid (H2SO4) truly deserves the title “King of Chemicals,” and its extensive use across various industries is no coincidence. This substance has become a vital component in the industrial world due to a unique combination of chemical and physical properties.
The main reasons for sulfuric acid’s widespread use and importance are:
Extremely Strong Acidic Nature: Sulfuric acid is a very strong inorganic acid that can react vigorously with bases and many metals. This strong acidic property makes it an excellent chemical reagent for neutralizing bases, removing oxides, and cleaning metal surfaces (in etching and descaling processes).
High Affinity for Water (Strong Dehydrating Agent): Sulfuric acid has a very strong tendency to absorb water. This characteristic leads to its use as a dehydrating agent in various chemical reactions (such as the production of alcohols, esters, and other organic compounds) and also for drying gases and liquids. This strong dehydrating property is also responsible for severe burns resulting from skin contact, as it draws water from tissues.
Oxidizing Power: Sulfuric acid, especially in higher concentrations and temperatures, is a potent oxidizing agent. This property allows it to be used in various oxidation processes, such as the production of sulfur dioxide, the oxidation of metals and non-metals, and also in the manufacture of explosives.
Inexpensive and Readily Available Production: Sulfur, as the primary raw material for sulfuric acid production, is an abundant and relatively inexpensive element. The manufacturing process for sulfuric acid is also well-developed and efficient, allowing for large-scale production at a reasonable cost, making it readily accessible to industries.
High Reactivity and Catalytic Capability: Sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst (a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed) in many reactions. This property allows industries to carry out production processes more quickly and efficiently.
Versatility in Concentrations: Sulfuric acid can be produced in various concentrations (from dilute to concentrated), each having its specific applications. This flexibility in concentration broadens its range of uses.
Due to this combination of properties, sulfuric acid plays a vital and indispensable role in numerous industries, including the production of chemical fertilizers (such as phosphate and sulfate fertilizers), detergents, dyes, pharmaceuticals, metal processing, oil and gas refining, battery manufacturing, and synthetic fibers. This is why a massive volume of the world’s sulfur is dedicated to its production.
Thanks for a marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed reading it,
you happen to be a great author. I will make sure to bookmark your blog and will often come
back sometime soon. I want to encourage one to continue your great posts, have a nice
day!
I really appreciate you taking the time to leave such a kind comment. I’m so glad you enjoyed the post and found the information useful!
Knowing that my work is helpful and enjoyable for readers like you is what keeps me going. Thanks for the encouragement, and I look forward to seeing you back on the site soon.
Have a great day!
There’s a delicate beauty in the way your words dance across the page, offering both depth and grace.
Thank you so much for your kind words. I’m truly grateful to hear that my writing resonated with you.
Sulfur is the fourth most important nutrient for plants. How does the added Bentonite in Bentonite Sulfur (as mentioned for agriculture) help the plant absorb the sulfur, given that plants absorb it as sulfate?
The Bentonite is a clay binder that swells when wet. It facilitates the disintegration of the solid sulfur prills into a fine powder when applied to the soil. This finer particle size significantly increases the surface area, allowing soil microbes to oxidize the elemental sulfur into the readily available sulfate form much faster, improving nutrient uptake efficiency.
Why is Petrochemical Sulfur the preferred choice over Mineral Sulfur for industrial and agricultural applications?
Petrochemical Sulfur (around 99.5% purity) is preferred due to its significantly higher purity and the absence of toxic contaminants (like aluminum and heavy metals) found in lower-purity Mineral Sulfur (10-40%).
Why is sulfur used in pharmacy to treat acne, and what is its mechanism of action on the skin?
Sulfur is a “keratolytic” agent; meaning it softens and sheds dead skin layers. This process unclogs pores and absorbs excess skin oil. Additionally, its mild antibacterial properties inhibit the growth of acne-causing bacteria.